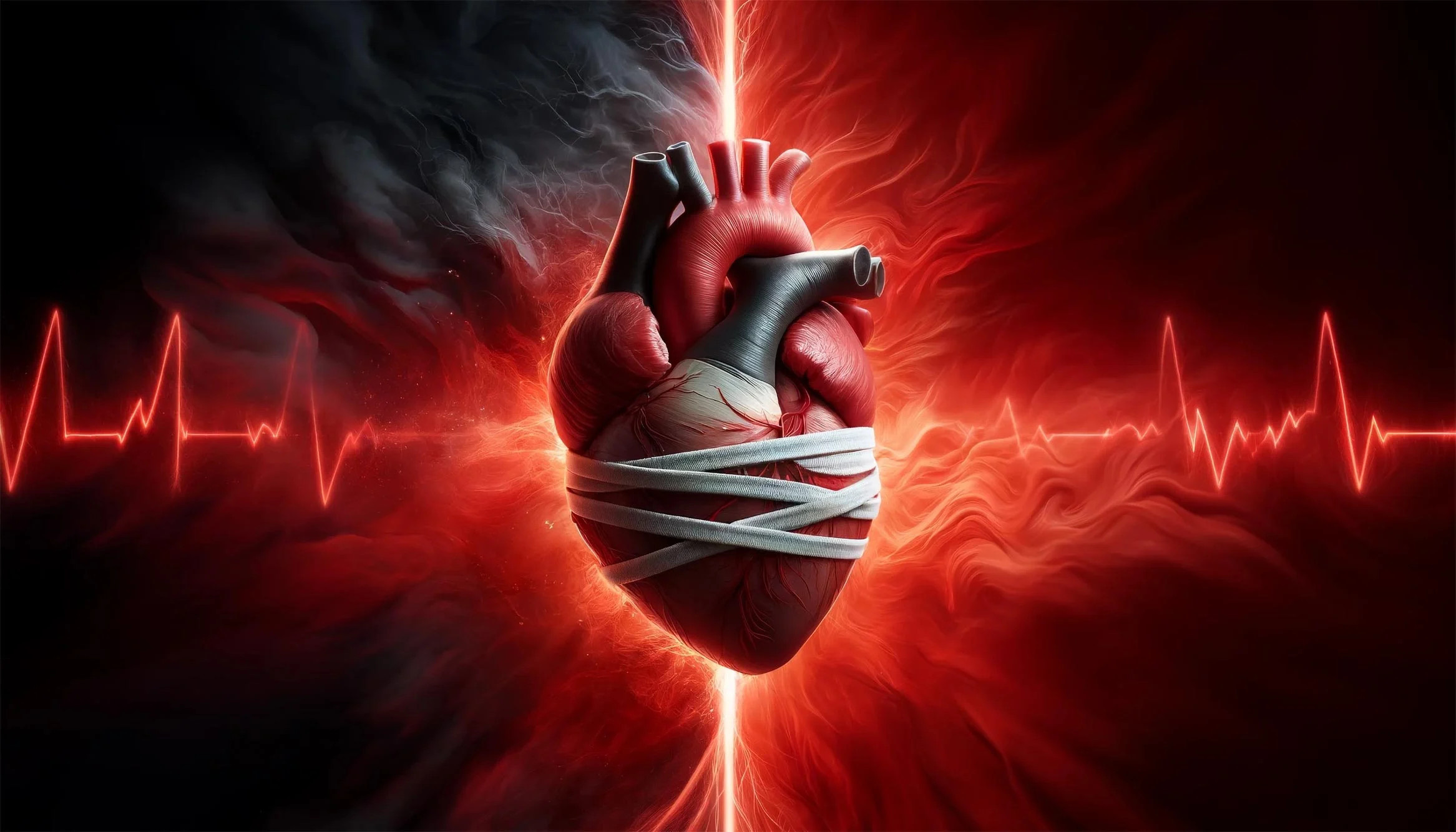
Understanding the Relationship Between Anger and Heart Health
Anger is a common human emotion, experienced by everyone at some point in their lives. While occasional anger is a natural response to certain situations, excessive or prolonged anger can have detrimental effects on both mental and physical health. Recent scientific studies have shed light on the connection between anger and heart health, revealing that intense bursts of anger could significantly increase the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
The Physiology of Anger
To understand how anger impacts heart health, it’s essential to examine the physiological responses that occur when we experience anger. When a person becomes angry, their body undergoes a series of changes known as the “fight or flight” response. This response triggers the release of stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which prepare the body to either confront the source of anger or flee from it.
During this process, heart rate and blood pressure increase, while blood vessels constrict, redirecting blood flow to vital organs and muscles. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, chronic anger can lead to sustained elevation of stress hormones, placing strain on the cardiovascular system and increasing the risk of heart disease.
The Link Between Anger and Heart Attacks
Several studies have investigated the association between anger and heart attacks, providing valuable insights into how emotional stressors can impact cardiovascular health. One such study, published in the European Heart Journal, found that individuals who experienced intense anger or emotional upset were at a significantly higher risk of suffering a heart attack in the subsequent hours.
Researchers analyzed data from multiple countries and observed a consistent pattern: episodes of intense anger were associated with a two to three-fold increase in the risk of myocardial infarction (heart attack) within two hours of the emotional outburst. This heightened risk was particularly pronounced in individuals with existing risk factors for heart disease, such as hypertension or a history of heart attacks.
Understanding the Mechanisms
While the exact mechanisms underlying the relationship between anger and heart attacks are not fully understood, researchers have proposed several potential explanations. One theory suggests that the physiological changes triggered by anger, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, can lead to the rupture of vulnerable plaques in the coronary arteries, causing a heart attack.
Additionally, chronic anger and hostility have been linked to unhealthy lifestyle behaviors that contribute to heart disease, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. Over time, these factors can take a toll on cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of heart attacks and other adverse outcomes.
Managing Anger for Heart Health
Given the significant impact of anger on heart health, learning to manage and cope with this emotion is essential for overall well-being. Various strategies can help individuals effectively deal with anger and reduce its negative effects on the heart:
- Deep Breathing and Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the body’s stress response and promote relaxation during moments of anger or frustration.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise not only improves cardiovascular health but also serves as a natural outlet for pent-up anger and stress. Activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can help release tension and improve mood.
- Seeking Support: Talking to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional can provide valuable support and perspective during times of anger. Expressing emotions in a healthy way can prevent them from building up and causing harm.
- Practicing Forgiveness: Holding onto anger and resentment can fuel negative emotions and harm mental and physical health. Learning to forgive oneself and others can release emotional burdens and promote emotional well-being.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques is crucial for maintaining heart health and reducing the impact of anger on the cardiovascular system.
Conclusion
While anger is a normal and unavoidable part of life, it’s essential to recognize its potential impact on heart health and take proactive steps to manage it effectively. By understanding the connection between anger and heart attacks and adopting healthy coping strategies, individuals can protect their cardiovascular health and lead happier, more fulfilling lives.